Important Question and Answer PHYSICS Class 12th MP BOARD 2026

Question 1 – What is Fundamental charge? What is its value?
Answer – The charge of a single electron is called the elementary charge.
Value: 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C.
Question 2 -Where Will an electron move towards a higher potential or a lower potential in an electric field? Why?
Answer – Towards a higher potential because the electron experiences a force in the opposite direction of the electric field.
Question 3 – What is an electric cell? Give examples.
Answer – A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Examples: Daniell cell, Leclanché cell
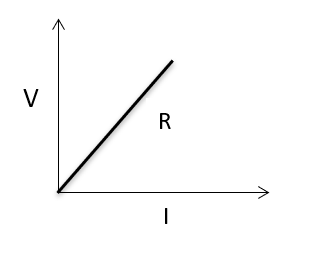
Question 4 – State Ohm’s law. And draw a graph between current and potential difference.
Answer – If the physical conditions of a wire are not changed, then the potential difference applied across its ends is directly proportional to the current flowing through it.
V=IR
Question 5 Why do magnetic field lines have no starting or ending points?
Answer – Magnetic field lines form closed curves.
Question 6- An electric bulb is designed to deliver 200 W of power at a 220 V supply. Find the resistance of the bulb.
Answer –
Given –
P = 200 W, V = 220 V
R = V^2/P = (220)^2/200
= (220 x 220)/200
= 232 Ω
Question 7- An electric bulb is designed to deliver 200 W of power at a 220 V supply. Find the rms current flowing through the bulb.
Answer – Since P = IV
I = 200W/220V
I = 20/22
I = 0.63 A
Question 8 What are conjugate foci?
Answer – Two points on the principal axis such that if an object is placed at the first point, an image is formed at the second point, and if an object is placed at the second point, an image is formed at the first point. Such points are called conjugate foci.
Question 9 Write two differences between a refracting telescope and a reflecting telescope.
Answer – Refracting Telescope Reflecting Telescope
(i) Spherical aberration occurs. (i) Spherical aberration does not occur.
(ii) The image is less bright. (ii) The image is brighter.
Question 10 What is the photoelectric effect? Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Answer – When light of a frequency greater than a certain frequency is incident on a metal surface, photoelectrons are emitted from the surface.
hv = hv0 + 1/2mV2max
Question 11 What are de Broglie matter waves? Write the de Broglie wavelength equation.
Answer – Every moving particle is associated with a wave, which is called a matter wave.
λ = h/P
MP BOARD 2026 PHYSICS CLASS12th Self Test ( Objective Types )
Question 12 Write any two postulates of Bohr’s model.
Answer – (i) An electron cannot revolve around the nucleus in just any orbit, but only in certain specific orbits.
(ii) An electron can only revolve in those orbits where its angular momentum is an integral multiple of h/2π.
Question 13 What are isotopes? Write any two isotopes of hydrogen.
Answer – Isotopes: Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei.
2/1 H, 3/1 H
Question 14 What are isobars? Give an example.
Answer – Isobars: All nuclei that have the same mass number A are called isobars.
3/1 H, 3/2 He
Question 15 Write two characteristics of electric field lines.
Answer –
(1) Electric field lines originate from positive charges and terminate on negative charges.
(2) Two electric field lines never intersect each other.
Question 16 Write two characteristics of an equipotential surface.
Answer –
(1) The electric potential is the same at every point on an equipotential surface.
(2) The work done in moving an electric charge from one point to another on an equipotential surface is zero.
Question 17 Write two differences between self-induction and mutual induction.
Answer – Self-induction Mutual induction
(1) The phenomenon of induced emf (1) The phenomenon of induced emf
in a single isolated coil due to in a second coil due to a change
a change in flux in the same coil in flux in the first coil is called mutual induction.
is called self-induction.
(2) The induced current affects the (2) The induced current does not affect the main current.
main current.
Question 18 Write two differences between a step-up transformer and a step-down transformer.
Answer – Step-up transformer Step-down transformer
(1) The output voltage is greater The output voltage is less than the input voltage.
than the input voltage.
(2) The secondary coil has more The secondary coil has fewer The coil has fewer turns.
turns than the primary coil.
Question 19 – Which waves are also called heat waves? What effect related to maintaining the average temperature on Earth do these waves play a crucial role in?
Answer – Infrared waves. Greenhouse effect.
Question 20 – Write the name and one use of the electromagnetic wave with the highest frequency.
Answer – Gamma ray.
Use: Destroying cancer cells in medicine.
Question 21 – If the lower half of the reflecting surface of a concave mirror is covered with an opaque material, what effect will this have on the image formed by the mirror of an object placed in front of it? Write the answer.
Answer – The image of the object will remain of full size,
but its intensity will be halved.
Question 22 – When a ray of light enters obliquely from an optically rarer medium to an optically denser medium, what will be the effect on the velocity and frequency of the light ray? Write the answer.
Answer – The velocity of the refracted ray will decrease, and its frequency will remain unchanged.
Question 23 – Write two conclusions obtained from the alpha particle scattering experiment.
Answer – (1) Most of the atom is empty space, and most of its mass is concentrated in a small volume of the atom called the nucleus.
(2) The total positive charge of the atom is in the nucleus, and electrons revolve around the nucleus in orbits.
Question 24 – Write two characteristics of nuclear forces.
Answer – (1) Nuclear force is much stronger than electrostatic forces and gravitational force.
(2) Nuclear forces do not depend on the nature of electric charges.
Question 25 Draw a labeled diagram of the electrical circuit for the forward biasing of a p-n junction diode.

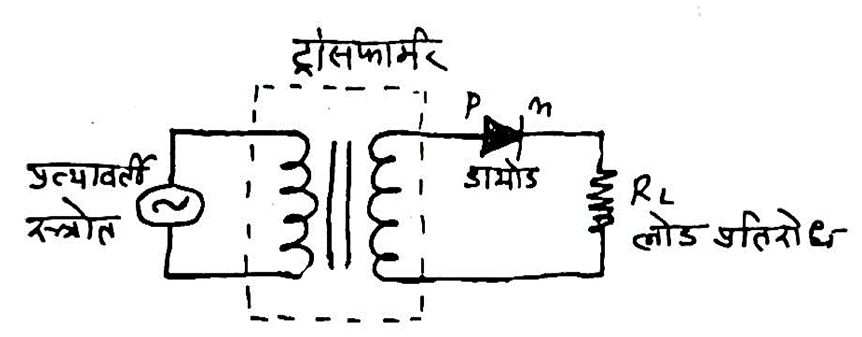
Question 25– Draw a labeled circuit diagram of a half-wave rectifier.
Question 26- Derive Coulomb’s inverse square law of electrostatics using Gauss’s law.
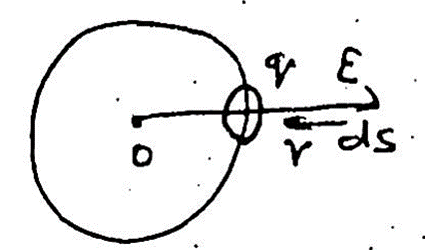
From electric flux
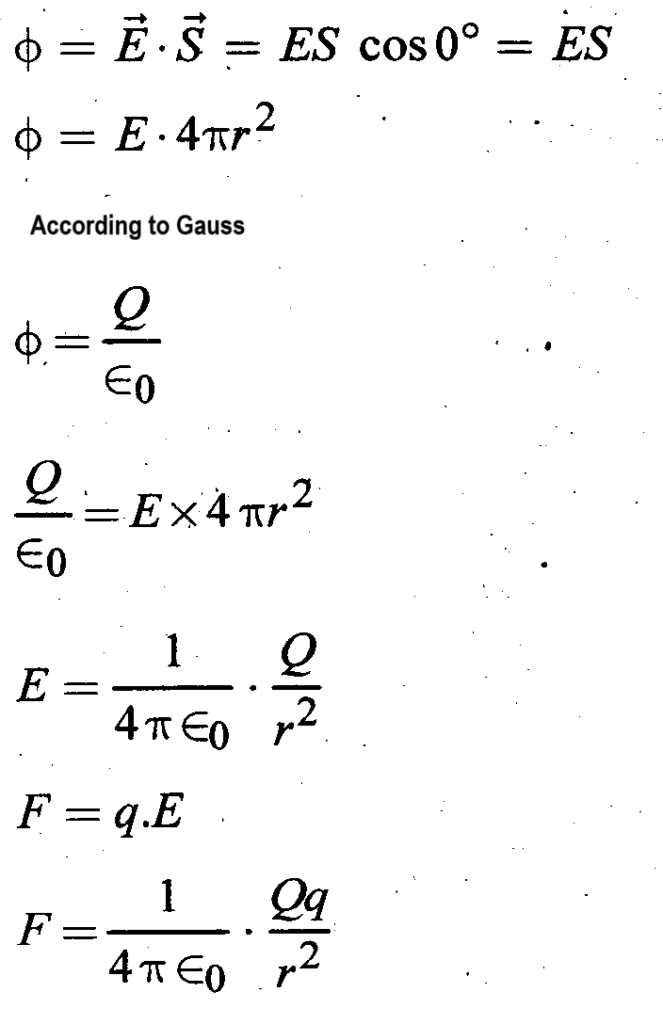
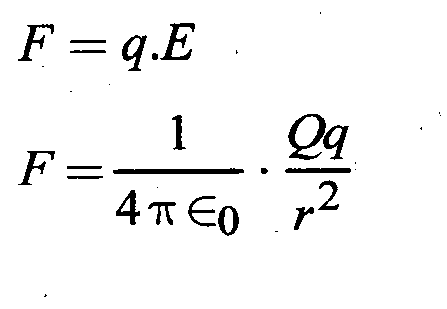
Question 27-What is meant by the capacitance of a conductor? Write down the factors affecting the capacitance of a conductor.
Answer – The capacitance of a conductor is equal to the amount of charge that causes a unit change in the potential of that conductor. C = Q/V
Factors:
(i) Increasing the size of the conductor increases the capacitance because the potential decreases.
(ii) The presence of another conductor near the conductor increases its capacitance because the potential decreases.
Question 28- Write any three differences between electromotive force and potential difference.
Answer – Electromotive force Potential difference
(i) It is equal to the work done by the cell (i) It is equal to the work done by the cell
in flowing a unit charge throughout the in flowing a unit charge only in the external
entire circuit. circuit.
(ii) It does not depend on the amount of (ii) It depends on the amount of
electrolyte. electrolyte.
(iii) It does not depend on the size of the (iii) It depends on the size of the
plates used in the cell and the distance plates used in the cell and the distance
between them. between them.
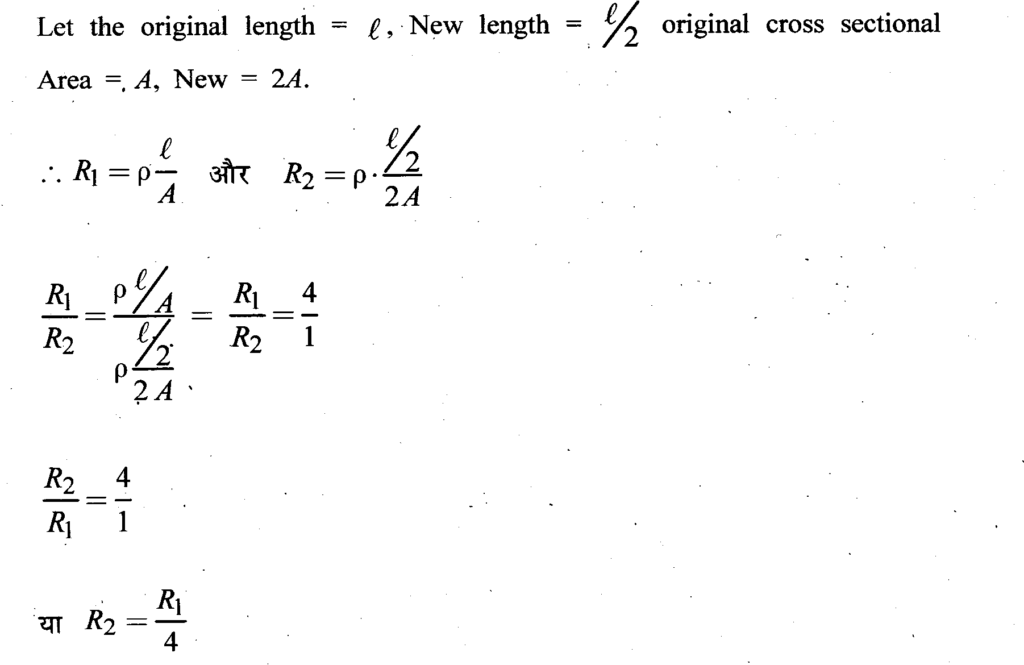
Question 29 – What will be the resistance of a conductor wire if its length is reduced to half of its original length and its cross-sectional area is doubled?
Ans-
Question 30- Describe the total internal reflection of light based on the following points:
(i) Labeled ray diagram
(ii) Definition
(iii) One application
Ans-
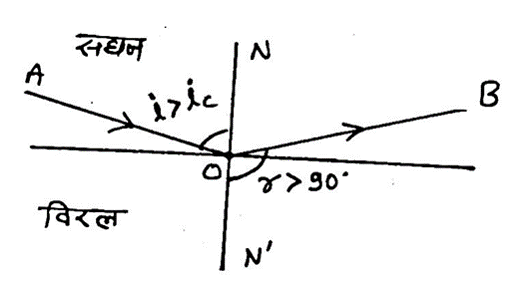
(ii) If a ray of light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium and strikes the interface at an angle greater than the critical angle, the ray does not enter the rarer medium but is reflected back into the denser medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection.
(iii) Optical fiber: In an optical fiber, the refractive index of the core material is greater than that of the outer cladding. Therefore, when an optical signal is introduced at a suitable angle, it undergoes multiple total internal reflections and emerges from the other end.
Question 31- Describe Huygens’ wave theory based on the following points:
(i) Definition of a wavefront
(ii) Ray diagram of a spherical wave emanating from a point source
(iii) Emission of secondary wavelets
Answer – (i) The locus of all points that oscillate in the same phase as the disturbance originating from a light source is called a wavefront.
ii.
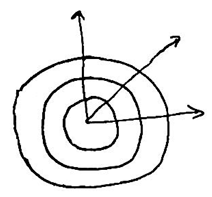
(iii) According to Huygens’ principle, every point on a wavefront is a source of secondary disturbance. The wavelets originating from these points spread out in all directions with the speed of the wave. These wavelets emanating from the wavefront are called secondary wavelets.
Question 32- Write three experimental observations of the photoelectric effect.
Answer – – (1) The photoelectric current (number of photoelectrons) is directly proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation.
(2) The kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is directly proportional to the frequency of the incident radiation.
(3) Photoelectric emission is an instantaneous process without any time lag.
Question 33- Write three characteristics of a photon.
Answer – (1) The energy of each photon is E = hν.
(2) Photons are not deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
(3) In photon-particle collisions, the total energy and total momentum are conserved.
Question 34- Write the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
Answer – Intrinsic Semiconductor Extrinsic Semiconductor
(i) Intrinsic semiconductors are pure (i) In semiconductors, other elements are added through the process of doping. Therefore, they are impure semiconductors.
semiconductors.
(ii) The number of electrons in the conduction (ii) In N-type, there is an excess of electrons, and
band is equal to the number of holes in the in P-type, there is an excess of holes.
valence band. ne = nh
(iii) Conductivity is low. (iii) Conductivity is high.
(iv) Si, Ge (iv) Made by adding arsenic and antimony to Si, Ge.
Question 35- What is a transformer? Explain its principle and the energy losses that occur in it.
Answer – – Transformer: A transformer is a device that converts AC voltage from one value to another, either higher or lower, without significant energy loss.
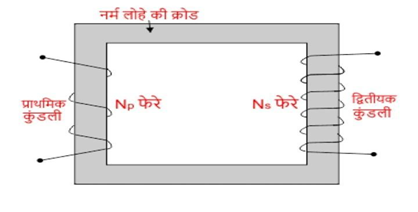
The induced EMF between the ends of the secondary coil with Ns turns.
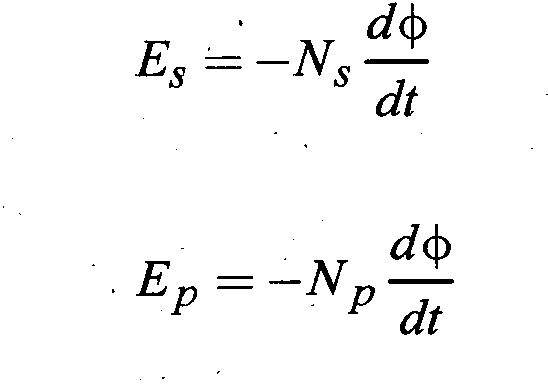
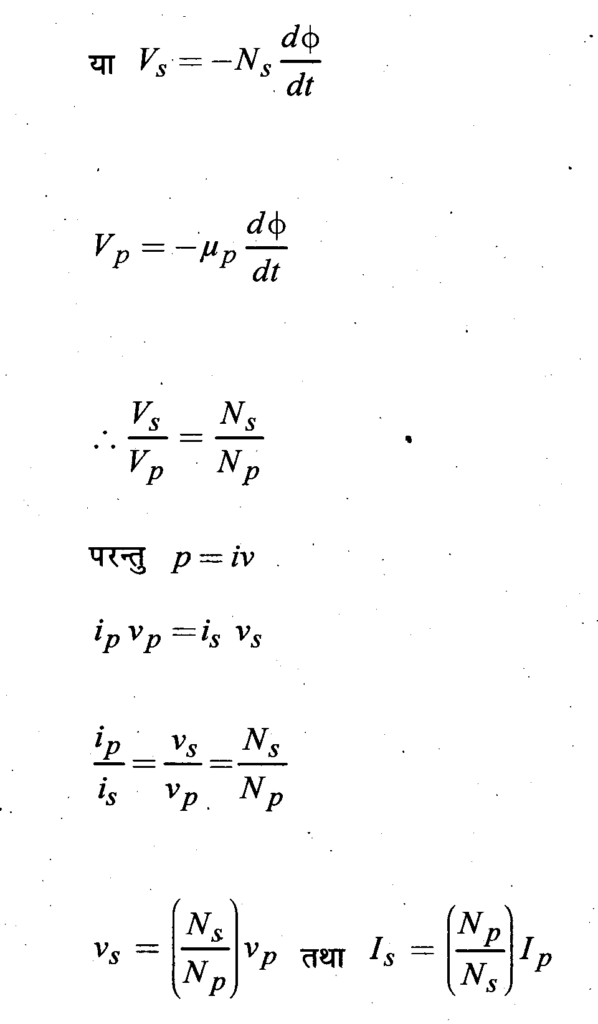
Energy Losses:
(i) Flux Leakage: Due to poor design or incorrect air gap, not all of the flux from the primary coil passes through the secondary coil.
(ii) Resistance of the Windings: Energy is lost due to heat generated in the wires. (I²R loss)
(iii) Eddy Currents: Eddy currents are induced in the iron core, causing it to heat up.
(iv) Hysteresis Loss: The magnetization is repeatedly reversed, and this energy appears as heat in the core.
This may Also Useful For You
MP BOARD 2026 PHYSICS CLASS12th Self Test ( Objective Types )
