MP BOARD 2026 – Class 12 BIOLOGY Important Questions and Answers
This post contains important questions from the Board of Secondary Education 2026 for Class 12 BIOLOGY. These important questions have also been asked in previous years’ exams. At the end of this post, you will also be able to solve objective-type self-tests useful for the 2026 exam.

MP BOARD 2026- Objective Question Based Self Test – BIOLOGY Class 12
Question 1 – What do you understand by triple fusion?
Answer – The second male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei in the central cell to form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus. This is called triple fusion.
Question 2 – What is emasculation?
Answer – The removal and expulsion of anthers from a flower bud with forceps before anther dehiscence in a bisexual flower is called emasculation.
Question 3 – What is parturition?
Answer – At the end of pregnancy, the fetus is expelled due to strong uterine contractions. This process of expulsion is called labor or childbirth.
Question 4 – What is colostrum?
Answer – The milk that is secreted during the first few days of lactation is called colostrum. It contains several types of antibodies.
Question 5 – Write the reasons for population explosion. (Any two)
Answer – (i) A sharp decline in the mortality rate.
(ii) An increase in the number of people of reproductive age.
Note: Marks may also be awarded for writing any two correct reasons in addition to the above.
Question 6 – Name any two sexually transmitted diseases.
Answer – STIs:
Gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, genital herpes, trichomonas, chlamydia, etc. (Name any two)
Question 7 – What is BOD (BOD)?
Answer – BOD refers to the amount of oxygen required when bacteria oxidize organic matter in one liter of water, consuming the organic matter. This amount of oxygen is called Biological Oxygen Demand.
Question 8 – What is the Ganga Action Plan?
Answer – The Ministry of Environment and Forests initiated the Ganga Action Plan to protect our country’s major rivers from pollution. Under this, only treated sewage will be discharged into rivers. Therefore, it is proposed to build a large number of new sewage treatment stations.
Question 9 – What is cloning?
Answer – Creating or creating replicated structures similar to a template DNA is called cloning. Or, the process of replicating a foreign DNA fragment and multiplying it in a host organism is called cloning.
Question 10 – What is a cry gene?
Answer – The gene that encodes toxins is called cry. Some strains of Bacillus urinariensis produce the toxic insecticidal protein 2Ve, encoded by Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab.
Question 11 – What causes AIDS? Write any two causes.
Answer – AIDS is caused by the following reasons:
(i) Sexual contact with an infected person.
(ii) Transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products.
(iii) By sharing infected needles, such as among drug users.
(iv) From an infected mother to her child through the placenta.
(2 points for any two reasons correctly)
Question 12 – How is cancer treated?
Answer – Cancer is usually treated by:
(1) Surgery.
(2) Radiation therapy.
(3) Chemotherapy is used to kill cancer cells.
(4) Most often, a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy is used.
(5) Interferon Y, which activates the immune system and helps destroy tumors.
(2 points for any two of the above treatments)
Question 13 – What is a histone?
Answer – A histone is a group of positively charged, alkaline proteins.
Question 14 – Which nitrogenous bases are found in RNA?
Answer – The following four nitrogenous bases are found in RNA:
(1) Adenine
(2) Guanine
(3) Uracil
(4) Cytosine
Question 15 – What is pedigree analysis?
Answer – Pedigree analysis is an important tool in human genetics. The concept of inherited disorders in human society has been around since ancient times. The history of a lineage is studied in relation to the inheritance of these traits. Such analysis of traits persisting over several generations is called pedigree analysis. It is used to detect specific traits, abnormalities, and diseases.
Question 16 – Write the difference between homozygous and heterozygous.
Answer – Homozygous Heterozygous
(1) Both alleles are identical
Both alleles are unequal
(2) Both dominant or both dominant
One dominant and one recessive
(3) Pure trait hybrid
Question 17 – What is amniocentesis? Write its significance.
Answer – Amniocentesis is a technique used to detect potential genetic diseases in an embryo before birth.
This test determines the health, sex, or genetic makeup of the developing embryo.
Significance: In case of abnormalities in the baby, abortion can be performed with the advice of a doctor.
Question 18 – What is MTP? Write its safe period.
Answer – The deliberate or voluntary termination of a pregnancy before the full term is called induced abortion or medical termination of pregnancy (MTP).
Safe period: MTP performed up to 12 weeks of pregnancy is considered quite safe.
Question 19 – What is a point mutation? Give an example.
Answer – A mutation that occurs due to a change in a single base pair of DNA is called a point mutation.
Example: Sickle cell anemia
Question 20 – A male human can never pass on the hemophilia gene to a son. Why?
Answer – The genes for the hemophilia trait are recessive and are located on the X chromosome, but the chromosome lacks its allele.
Since males can develop the disease even if they have only one X chromosome, the recessive gene is absent.
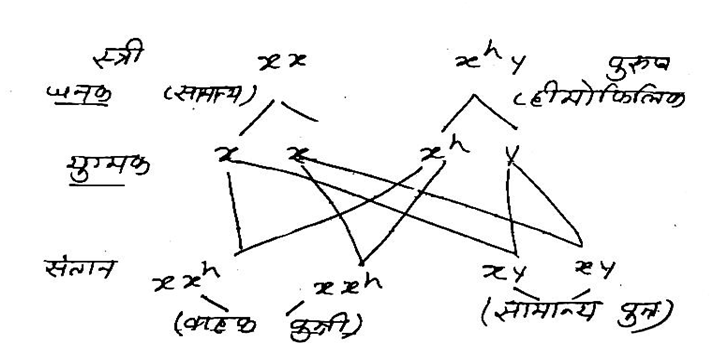
Question 21 – What is adaptive radiation? Give an example.
Answer – The process of evolution of different species in a particular geographic region, starting from one point and spreading to other geographic regions, is called adaptive radiation.
Example: Darwin’s finch is a prime example of this phenomenon.
Question 22 – Write the Hardy-Weinberg law.
Answer – In a population, allele frequencies and their loci are stable.
They remain constant from one generation to the next, and the gene pool always remains unchanged. This is called genetic equilibrium.
p² + 2Pq + q² = 1
The binary expression of (p + q)²
Here P represents the allele A.
Here q represents the q allele.
Question 23 – Why are cyanobacteria considered beneficial in rice fields?
Answer – Cyanobacteria are autotrophic microorganisms. They are widely found in aquatic and terrestrial environments. They can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Cyanobacteria play an important role as biofertilizers in rice fields. They increase organic matter, thereby improving soil fertility.
Question 24 – Why are there large pores in Swiss cheese?
Answer – The large pores found in Swiss cheese are caused by the large amounts of CO₂ produced by a bacterium called Propioni bacterium scharmannii.
Question 25 – What is a biopatent (bioright)?
Answer – A biopatent is the registration or patenting of a product, technology, or process made using genetic material, plants, and other biological resources.
Question 26 – What is golden rice? Write about it.
Answer – Golden rice is a genetically modified crop. It helps compensate for vitamin A deficiency in people living in areas where rice is the staple food. It contains the gene for B-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, in recombined DNA. Technology may have been introduced, which gave this rice a yellowish color. Therefore, it is called Sunhura rice.
Question 27 – What do you understand by population density?
Answer – Population density indicates the size of a population. The total number of populations in a given area at a given time is called the population density of that area.
Population density = (total number of organisms) / (area)
D = N / S
D = density
S = area of the area
N = number of organisms
Question 28 – Define camouflage and give an example.
Answer – Predatory species have developed various defense mechanisms to reduce the impact of predation.
Some species of insects and frogs are cryptically colored to avoid being easily detected by predators, a practice known as camouflage.
For example, the Monarch butterfly possesses special chemicals on its body that make it unpalatable to its predators.
Question 29 – What is a hot spot? Name a hot spot in India.
Answer – Areas with high species richness and high endemism are called hotspots.
Name of hotspot:
(1) Western Ghats
(2) Eastern Himalayas
(3) Indo-Varma
Question 30 – Name the three essential components of biodiversity.
Answer – (1) Genetic diversity: When variation occurs at the genetic level.
Example: Raubolfia bomitoria, a medicinal plant found in the Himalayas.
(2) Physiological diversity: This variation occurs at the species level.
Example: The Western Ghats have a greater diversity of amphibian species than the Eastern Ghats.
(3) Ecological diversity: This variation occurs at the ecosystem level.
Example: The deserts of India.
Question 31 – Give a diagrammatic representation of oogenesis. (Figure)
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 32 – What is amniocentesis? Write its uses.
Answer – Amniocentesis is a testing method in which amniotic fluid is extracted from the mother’s uterus using a syringe. The fluid is then analyzed for various genetic disorders in the fetus, including Down syndrome, hemophilia, color blindness, and sickle cell anemia.
Question 33 – What is a test cross? Show its diagrammatic representation.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 34 – Draw a labelled diagram of Miller’s experiment.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 35 – Write down ways to prevent alcohol and drug abuse among adolescents.
Answer – The following are ways to prevent adolescents from using alcohol and drugs:
(1) Every adolescent has their own personality. They should not be unnecessarily pressured to perform activities beyond their threshold.
(2) Education and counseling should also be provided to teach them how to cope with pressure. Counseling should be provided.
(3) Solving a teenager’s problems or concerns with the help of parents and peers can also help them avoid substance abuse.
(4) Professional and medical assistance can also help them break the habit of using these substances.
(5) Watch for signs of danger. If you see a friend or acquaintance using these substances, inform their teacher and parents for their own benefit.
(Write any three ways and give 3 points.)
Question 36 – How do microorganisms function as biofertilizers?
Answer – Biofertilizers are a type of organism that enhances the nutrient quality of the soil. Rhizobium bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into organic form, which plants absorb as nutrients. Other bacteria live in the soil, fixing N2 and increasing the soil’s N2 content. Mycorrhizae absorb phosphorus from the soil. Such symbiotic relationships contribute to pathogen resistance, salinity tolerance, and other factors. Blue-green algae also increase soil organic matter, thereby increasing fertility.
Question 37 – Write about the three major abiotic factors of the environment.
Answer – The three main abiotic factors of the environment are:
(1) Light –
Producing food through photosynthesis; describing autotrophy, photoperiodism, and light in the depths of the ocean.
(2) Temperature –
Flora and animals are found depending on the temperature.
Urothermal and stenothermal, etc.
(3) Water –
The most essential component; life is impossible without it. Plants and animals found in salty and freshwater are also different. In deserts, where water is scarce, plants and animals have different adaptations. Even in snow-covered areas, the flora and fauna are different.
Question 38 – What is decomposition?
Answer – Decomposition – They help break down complex organic material into inorganic elements such as CO₂, water, and nutrients. This process is called decomposition. Dead plant remains, dead animal remains, and feces, etc., serve as raw materials for decomposition. The main stages of decomposition are fragmentation, leaching, reduction, humus formation, mineral formation, etc. Detritivores, fungi, and bacteria complete this process, resulting in the accumulation of organic matter.
Question 39 – Why are human testes located outside the abdominal cavity? Name the sac within which they are located.
Answer – The temperature required for the process of spermatogenesis, i.e., for sperm production in the testes, is 2-2.5 degrees Celsius lower than human body temperature.
The name of the sac is the scrotum.
Note: Marking is also written for questions with either or because the basis for scoring questions with or differs in some cases.
Question 40 – Draw a neat labeled diagram of a schematic section of the female reproductive system.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 41 – What is a monohybrid cross? Explain with a diagram.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 42 – What is co-dominance? Explain with an example.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 43 – Write three differences between biological pesticides and chemical pesticides.
Answer – Biological pesticides Chemical pesticides
(1) Do not pollute the environment.
(1) They do pollute.
(2) Do not harm non-target insects.
(2) They do harm.
(3) Are cheap.
(3) Are expensive.
(4) Harmful to food, fiber, and animal feed.
(4) Leaves harmful residues.
No residues are left, which are harmful to health.
Note: Marks will be awarded for writing any three differences.
Question 44 – Draw a neat labeled diagram of a biogas plant.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 45 – Why is the energy pyramid always upright? Explain.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 46 – Describe the relationship between productivity, gross primary productivity, and net productivity.
Answer – Productivity: The rate at which a trophic level in an ecosystem synthesizes energy-rich organic matter per unit area and per unit time is called the productivity of that trophic level.
Productivity –
I Gross Primary Productivity
II Net Productivity
Gross Primary Productivity: Gross primary productivity is the rate of complete absorption of energy by primary producers or the rate of total production of organic matter and biomass.
Net Productivity: The rate of complete absorption of energy by primary producers, or the rate of total production of organic matter and biomass, is called gross primary productivity.
Net Productivity: The rate of biomass or energy remaining after respiration by producers is called actual or net primary productivity.
Net Primary Productivity = Gross Primary Productivity – Respiration Rate
NPP = GPP – R
Question 47 – Explain the difference between microsporogenesis and megasporogenesis. What type of cell division occurs during these events? Name the structures formed at the end of both events.
Answer –
Microspore Reproduction
(1) In this process, a microspore is formed in the anther.
(2) In this process, a megaspore mother cell is formed.
(3) Many microspore mother cells are formed.
(4) A large number of microspores are formed.
(5) Three inactive and only one functional megaspore is formed.
Cell division
Meiosis
- Microspores are formed at the end of microsporogenesis.
- Megaspores are formed at the end of megaspore reproduction.
Question 48 – Draw a neat labeled diagram of a typical angiosperm ovule.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 49 – Write the characteristics of the genetic code.
Answer – The characteristics of the genetic code are:
(1) They are universal.
(2) They are degenerate.
(3) They are specific and unambiguous.
(4) Codons are triplets.
(5) They are comma-free. They do not stop midway.
(6) The AUG start codon occurs as an AUG, etc.
Question 50 – When a homozygous yellow- and round-seeded pea plant is crossed with a homozygous green- and wrinkled-seeded pea plant, calculate the phenotype ratio of the offspring obtained in the F2 generation using a checkerboard pattern.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 51 – How did Hershey and Chase differentiate between DNA and protein during their experiment to prove that DNA is the genetic material?
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 52 – Describe the disease AIDS in the following points:
(i) The full name of AIDS
(ii) The name of the pathogen that causes AIDS
(iii) Four ways to prevent AIDS
Answer –
(i) Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
(ii) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
Preventive measures:
(i) Avoid promiscuous sexual relations. (ii) Single-use needles should be used.
(iii) Shaving razors, blades, toothbrushes, etc., used by others should not be used.
(vi) The general public should be informed about the dangers and precautions of AIDS.
Note: Marks may also be awarded for writing about other measures.
Question 53 – Describe the polymerase chain reaction with a diagram.
Answer: Please write your own answers. (They will be uploaded to the site as soon as they become available.)
Question 58 – Write a note.
(a) Biopiracy
(b) Restriction enzymes
Answer –
(a) Biopiracy –
The use of biological resources by multinational companies and other organizations without systematic approval and compensation from a nation or its people is called biopiracy.
Traditional knowledge can be used for modern purposes through the use of biological resources. Therefore, some nations are enacting regulations prohibiting the use of their biological resources and traditional knowledge without prior permission to prevent biopiracy.
(b) Restriction Enzymes –
In 1963, two enzymes were isolated that inhibit bacteriophage growth in E. coli. One of these adds a methyl group to DNA, while the other cleaves DNA. In their nomenclature, the first word refers to the genus, and the second and third words are derived from the species of prokaryotic cells. For example, ECORI. There are two types:
Exonucleases and Endonucleases –
Exonucleases remove nucleotides from the DNA ends, while endonucleases cleave sites within DNA. and identify sequences of palindromic nucleotides.
Question 54 – Describe the ecosystem of a pond.
Answer – Ecosystem of a pond –
A pond is a shallow body of water in which water is the abiotic component. Organic, inorganic, and soil components accumulate at the bottom. Conditions such as solar input, temperature, and day length regulate the rate of activity of the pond. All trophic levels of the biotic component are found.
Producers – Phytoplankton, algae, submerged plants, marginal plants on the banks, etc.
Consumers – Zooplankton, free-floating and bottom-dwelling plants and animals, such as small and large fish, and other aquatic organisms.
Decomposers – Fungi and bacteria are found in abundance at the bottom of the pond. They decompose all dead plants, plankton, and all dead aquatic organisms.
Question 55 – How does plant succession occur on bare rock? Explain.
Answer – Succession on bare rock:
Biological communities are dynamic and change over time. These changes are gradually sequenced and form ecological succession.
(1) Lichen species are the first to appear on bare rocks. They secrete acids to dissolve the rocks and help form soil. They are called root explorers or pioneers.
(2) Floods bring plants like biophytes, which establish themselves even in shallow soil.
(3) These then give rise to larger plants, shrubs, ferns, vines, etc. Then come larger plants and trees.
(4) Finally, a forest community is formed, called a climax community. It persists until the environment changes. Over time, it transforms into xerophytes or mesophytes.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
You may also find this useful –
MP BOARD 2026- Objective Question Based Self Test – BIOLOGY Class 12
